In the fast-evolving world of financial technology, issuer processors play a critical role in ensuring seamless payment transactions across the United States. Whether you’re swiping a credit card at a retail store, making an online purchase, or using a mobile payment app, issuer processors work behind the scenes to facilitate secure and efficient transactions.
An issuer processor connects card issuers, like banks, to card networks, approving or declining credit/debit transactions securely and efficiently.
This article explores the role, functions, and significance of issuer processors, tailored for an American audience seeking to understand the backbone of modern payment systems.
The Role of Issuer Processors
Issuer processors serve as the technological bridge between card-issuing banks and the broader payment network, which includes merchants, acquirers, and card networks like Visa, Mastercard, and American Express. Their primary responsibilities include:
- Transaction Authorization: When a cardholder initiates a transaction, the issuer processor verifies the card’s validity, checks for sufficient funds or credit, and assesses fraud risks in real time. For example, if you use a Visa card at a coffee shop, the processor ensures the transaction is legitimate before approving it.
- Data Management: Issuer processors manage cardholder data, including account balances, transaction histories, and personal details, while adhering to strict security standards like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
- Fraud Detection and Prevention: With cybercrime on the rise, issuer processors deploy advanced algorithms and machine learning to detect suspicious activities. In 2024, fraud losses in the U.S. were estimated at $12 billion, making robust fraud detection a top priority.
- Settlement and Clearing: After a transaction is authorized, the processor facilitates the transfer of funds from the cardholder’s account to the merchant’s bank, ensuring accurate and timely settlement.
- Compliance and Reporting: Issuer processors ensure that transactions comply with federal regulations, such as those set by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), and provide detailed reports to issuers for auditing and customer service purposes.
How Issuer Processors Fit into the U.S. Payment Ecosystem
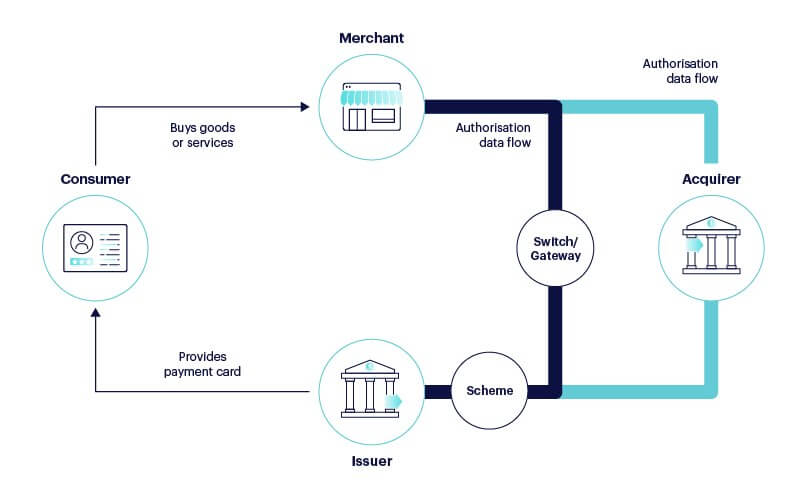
To understand the role of issuer processors, it’s helpful to visualize the broader payment ecosystem in the U.S. When a consumer makes a purchase, multiple parties interact:
- Cardholder: The individual using a credit, debit, or prepaid card.
- Merchant: The business accepting the card payment.
- Acquiring Bank: The merchant’s bank, which receives the payment.
- Card Network: Companies like Visa, Mastercard, or Discover, which set rules and facilitate communication.
- Issuing Bank: The financial institution that issued the card to the consumer.
- Issuer Processor: The technology provider that supports the issuing bank.
For instance, when you buy groceries using a Chase-issued Mastercard, the issuer processor (e.g., Fiserv or TSYS) handles the transaction on behalf of Chase, ensuring it’s processed securely and efficiently. This process happens in milliseconds, showcasing the technological prowess of issuer processors.
Major Issuer Processors in the USA
The U.S. is home to several leading issuer processors, each offering specialized services to banks and credit unions. Some of the key players include:
- Fiserv: A global leader in financial technology, Fiserv processes millions of transactions daily for banks like Wells Fargo and Bank of America. Its solutions include real-time fraud detection and cloud-based processing platforms.
- TSYS (Total System Services): Now part of Global Payments, TSYS is a major player in issuer processing, serving clients like Capital One. It specializes in scalable solutions for credit and debit card processing.
- Fidelity National Information Services (FIS): FIS provides issuer processing for a wide range of financial institutions, focusing on digital transformation and mobile payment integration.
- Jack Henry & Associates: Known for serving community banks and credit unions, Jack Henry offers tailored issuer processing solutions for smaller institutions.
These companies compete in a market driven by innovation, security, and customer experience. In 2024, the U.S. issuer processing market was valued at approximately $10 billion, with a projected annual growth rate of 7%, according to industry reports.
Challenges Faced by Issuer Processors
Despite their critical role, issuer processors face several challenges in the U.S. market:
- Rising Fraud Threats: As digital payments grow, so do sophisticated fraud schemes like card-not-present (CNP) fraud, which surged by 20% in 2023. Issuer processors must continuously upgrade their security protocols to stay ahead of cybercriminals.
- Regulatory Compliance: The U.S. has stringent regulations governing financial transactions, including the Durbin Amendment, which caps debit card interchange fees, and CFPB rules on consumer protection. Staying compliant while maintaining efficiency is a balancing act.
- Technological Advancements: The rise of contactless payments, mobile wallets (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Wallet), and cryptocurrencies demands that issuer processors adopt cutting-edge technologies like blockchain and tokenization.
- Consumer Expectations: American consumers expect fast, seamless, and secure transactions. A 2024 survey by PYMNTS found that 68% of U.S. consumers abandon transactions if they take longer than 3 seconds, putting pressure on processors to optimize performance.
The Future of Issuer Processing in the USA
The issuer processing landscape is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors. Here are some trends shaping the future:
- Real-Time Payments: The Federal Reserve’s FedNow Service, launched in 2023, is pushing real-time payment capabilities. Issuer processors are adapting to support instant fund transfers, which could redefine how Americans pay and receive money.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning are revolutionizing fraud detection and customer service. For example, issuer processors use AI to analyze transaction patterns and flag anomalies instantly, reducing false positives and improving user experience.
- Embedded Finance: The integration of financial services into non-financial platforms (e.g., Uber offering debit cards) is gaining traction. Issuer processors are enabling these partnerships by providing flexible APIs and white-label solutions.
- Sustainability and Inclusion: As ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) principles gain importance, issuer processors are exploring eco-friendly practices, such as reducing paper statements, and supporting financial inclusion by enabling prepaid cards for underbanked populations.
Why Issuer Processors Matter to American Consumers
For the average American, issuer processors may seem invisible, but their impact is profound. They ensure that your debit card works at the gas station, your credit card is secure during online shopping, and your mobile payment app processes transactions instantly. Without issuer processors, the convenience of modern payments would grind to a halt.
Moreover, issuer processors contribute to financial empowerment. By supporting prepaid cards and digital wallets, they help underserved communities access the financial system. In 2023, 4.5% of U.S. households were unbanked, according to the FDIC, and issuer processors play a role in bridging this gap through innovative payment solutions.
Choosing the Right Issuer Processor for Financial Institutions
For banks and credit unions, selecting an issuer processor is a strategic decision. Key considerations include:
- Scalability: Can the processor handle growing transaction volumes?
- Security: Does it offer robust fraud prevention and compliance with PCI DSS?
- Integration: Can it seamlessly integrate with existing systems and support new technologies like mobile wallets?
- Cost: What are the processing fees, and do they align with the institution’s budget?
For example, a regional credit union might choose Jack Henry for its community-focused solutions, while a national bank like Citibank might opt for Fiserv’s comprehensive platform.
Conclusion
Issuer processors are the unsung heroes of the U.S. payment ecosystem, enabling billions of transactions annually with speed, security, and reliability. As digital payments continue to dominate—projected to reach $9 trillion by 2027—issuer processors will play an even more critical role in shaping the future of finance. From combating fraud to supporting real-time payments and embedded finance, these technology providers are at the forefront of innovation. For American consumers, businesses, and financial institutions, understanding the role of issuer processors is key to navigating the complex world of payments with confidence.
FAQs
What is an example of an issuer processor?
Fiserv is an example of an issuer processor, helping banks like Wells Fargo process card transactions securely and efficiently.
What is the difference between issuer processor and acquirer processor?
Issuer processors support card-issuing banks; acquirer processors help merchants’ banks accept payments, ensuring smooth transactions between both sides.
What is the issuer processing platform?
An issuer processing platform is technology that helps banks manage card transactions, ensuring security, authorization, and settlement.
What is the issuing payment processor?
An issuing payment processor is a company that helps banks issue cards and process transactions quickly and securely.
Is Chase an issuer?
Yes, Chase is an issuer, a bank that provides credit and debit cards to customers for making payments.
Is Jack Henry an issuer processor?
Yes, Jack Henry is an issuer processor, providing technology to community banks for secure card transaction processing.











